What Is Redis?
Redis (REmote DIctionary Server) is an open-source, in-memory key-value database.
It stores data primarily in RAM, making it extremely fast.
It supports multiple data structures such as strings, lists, sets, and hashes, and is widely used for caching, real-time analytics, and session storage.
- Default port: 6379/tcp
- Type: In-Memory Database
- Modes: Standalone, Master-Slave Replication, Cluster
Nmap Scan
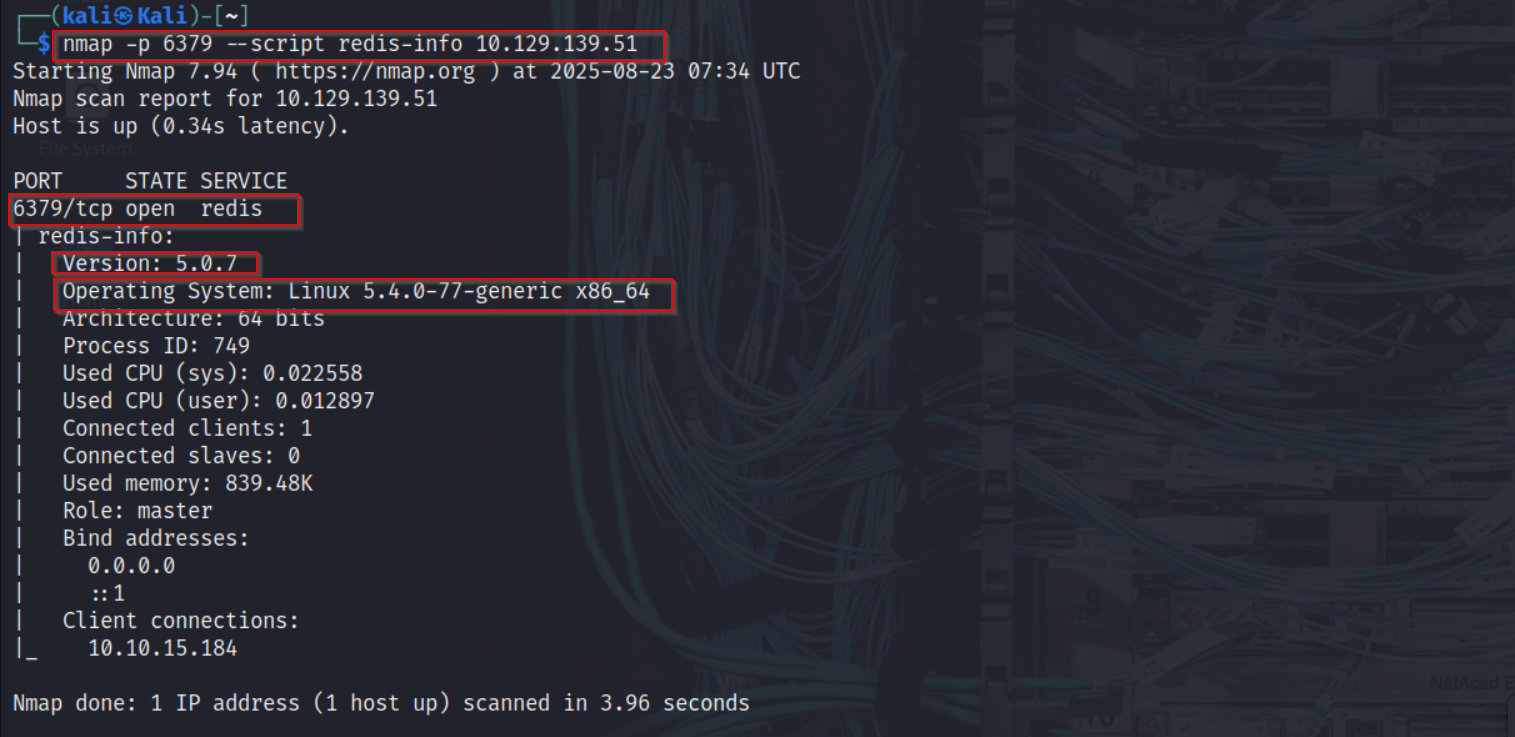
To start, I performed an Nmap scan to check for an exposed Redis service:
1
| nmap -p 6379 --script redis-info 10.129.164.202
|
1
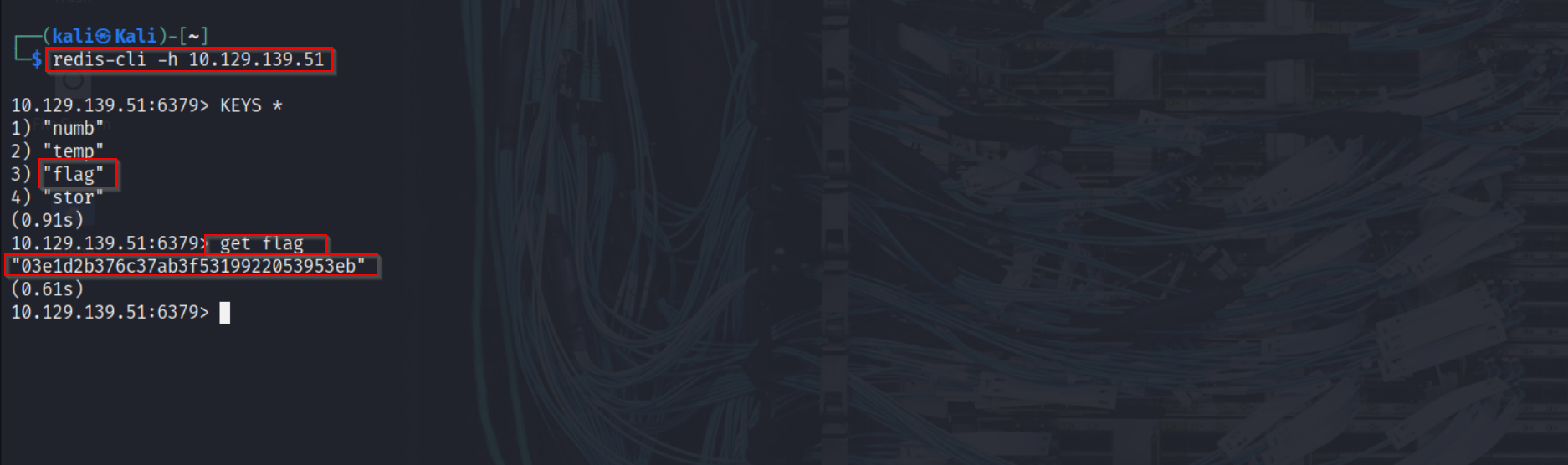
| redis-cli -h 10.129.139.51
|
Enumerating Redis
1
2
3
| Listing Keys
KEYS *
|
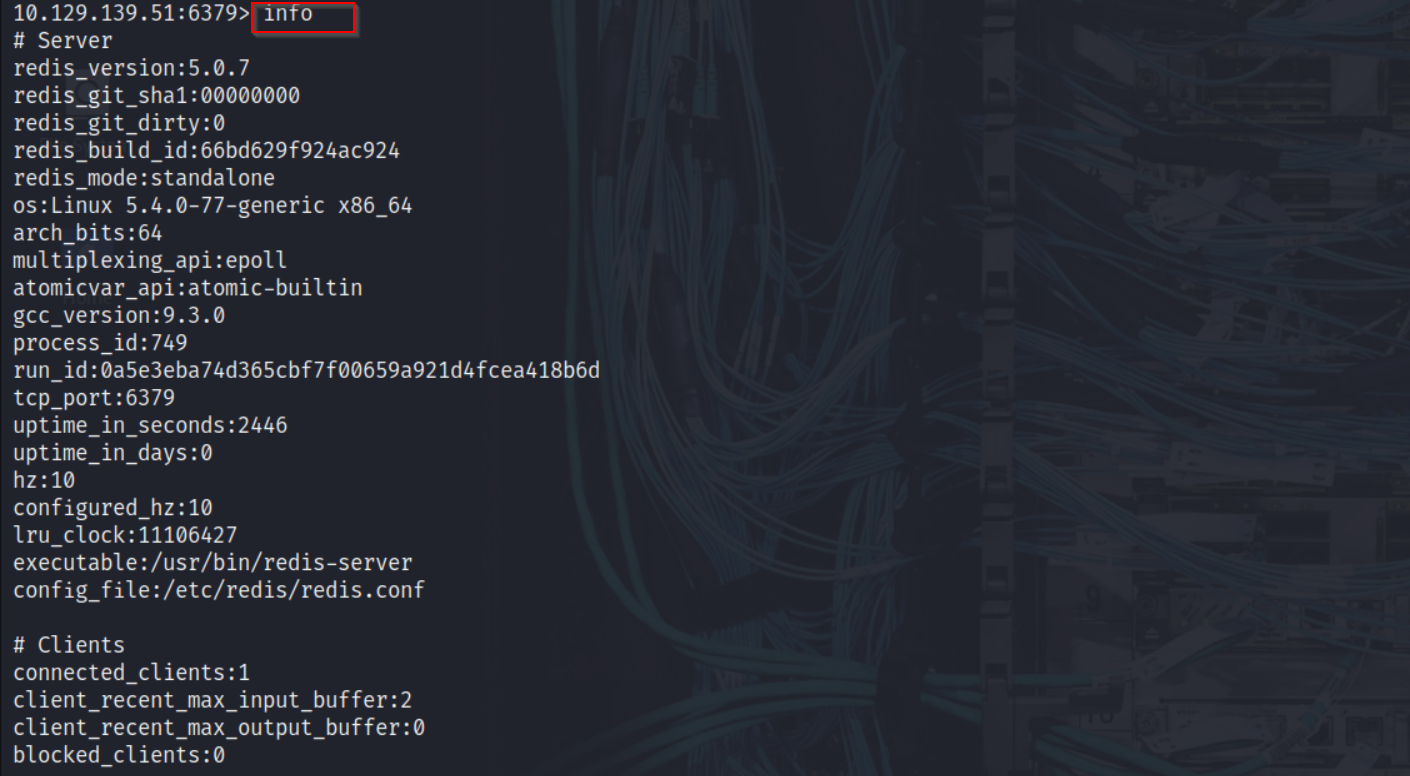
Checking Server Info
This command revealed server details, memory usage, connected clients, replication role, and more.
Retrieving Data The most interesting key was flag. Using the GET command:
GET flag Result:
Other Useful Redis Commands
During enumeration, several other Redis commands proved useful:
Check key type
1
2
3
| TYPE <key>
Check if a key exists
EXISTS <key>
|
1
2
| List all databases and keys
INFO keyspace
|
1
2
| Retrieve all elements of a list
LRANGE <key> 0 -1
|
1
2
3
| Retrieve all members of a set
SMEMBERS <key>
|
1
2
3
| Retrieve all fields and values of a hash
HGETALL <key>
|
1
2
3
| Switch databases
SELECT <db_number>
|